Effects of the Covid-19 Measures on the Economy and the Environment
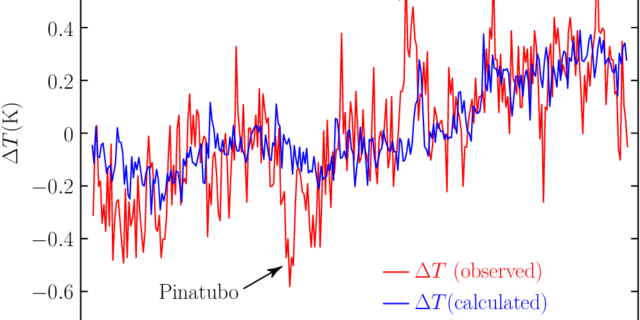
Peter Stallinga & Igor Khmelinskii September 29, 2021 Abstract The effects of the Covid-19 pandemic and governmental countermeasures are described in this work by putting it in the framework of the Energy Theory of Value. It is found that the downturn in economy is not accompanied by an equal downturn in energy consumption nor of carbon emissions. Moreover, not even the empirical fifth-power law linking the former two is any longer sustained, more so proving the state of virtualization of our economy (disconnecting it from a physical reality). It is also found that the reduction of carbon emissions had no …